# 第 11 章:再转换一次,就很自然
接下去,本文将结合实际日常编程应用,讨论 Natural Transformations 。Natural Transformations 恰巧是范畴论的支柱,是利用数学知识分析、重构代码不可或缺之技巧。事先申明,因作者知识水平所限,本文如有纰漏不实,还望海涵。好了,让我们开始吧。
# 令人生厌的嵌套
我想要提出一个关于嵌套的问题。但不是那种马上会唤起老母亲整理打扫天性的那种问题,而是我们马上会在之后的章节中遇到的问题。在任何情况下,我所谓的嵌套是将不同的两个类型套在同一个值上,某种意义上,看上去就像一个全新的类型。
Right(Maybe('b'));
IO(Task(IO(1000)));
[Identity('bee thousand')];
现在,我们用一些精心制作的例证来说明仿佛我们已经能够摆脱这些常见的嵌套情形。但是实际上我们编码的时候,不同的类型就像耳机线一样乱成一团,仿佛一种恶魔召唤的邪恶产物。如果我们编码的时候不是一丝不苟地组织正在使用的类型,最后代码会比猫咪咖啡厅的披头族更加难以理解。
# 一场情景喜剧
// getValue :: Selector -> Task Error (Maybe String)
// postComment :: String -> Task Error Comment
// validate :: String -> Either ValidationError String
// saveComment :: () -> Task Error (Maybe (Either ValidationError (Task Error Comment)))
const saveComment = compose(
map(map(map(postComment))),
map(map(validate)),
getValue('#comment'),
);
让类型声明形同虚设的坏家伙们都在这里了。容我稍微解释一下这一段代码。一开始,用getValue('#comment')获取用户输入,这是一个action,从一个element中获取文本。但是可能会因为字符串值不存在而获取失败,从而返回Task Error(Maybe String)。在这之后,我们需要map所有Task和Maybe传递文本到validate。最后,我们不是得到ValiadtionError或者想要的String。然后,从过层层 map,把当前Task Error(Maybe(Either ValidationError String))中的String传入postComment,最后返回Task的结果。
简直乱得骇人。一大堆抽象类型乱得像一幅业余表现主义的烂作,还混杂着波洛克式的多态,蒙德里安风的大统一。对于这种常见的情况,有许多解决方法。把这些类型编好弄成一个巨大的容器,分类后再join,将其同化,解构,等等。在下一章的重点,就在于通过 Natural Transformations 将他们同化。
# 全都很自然
Natural Transformations是“functor 之间的态射”,就是,一个操作容器本身的函数。类型上来说,它是个函数(Functor f, Functor g) => f a -> g a。让这个函数特殊的是,在任何情况下,都不能得知 functor 中的内容。就像两个党派交换机密文件,都会把东西封在马尼拉纸信封里,戳上“最高机密”。这是一个结构上的操作。functor 外壳的变化。形式上,Natural Transformations 作用于如下功能:
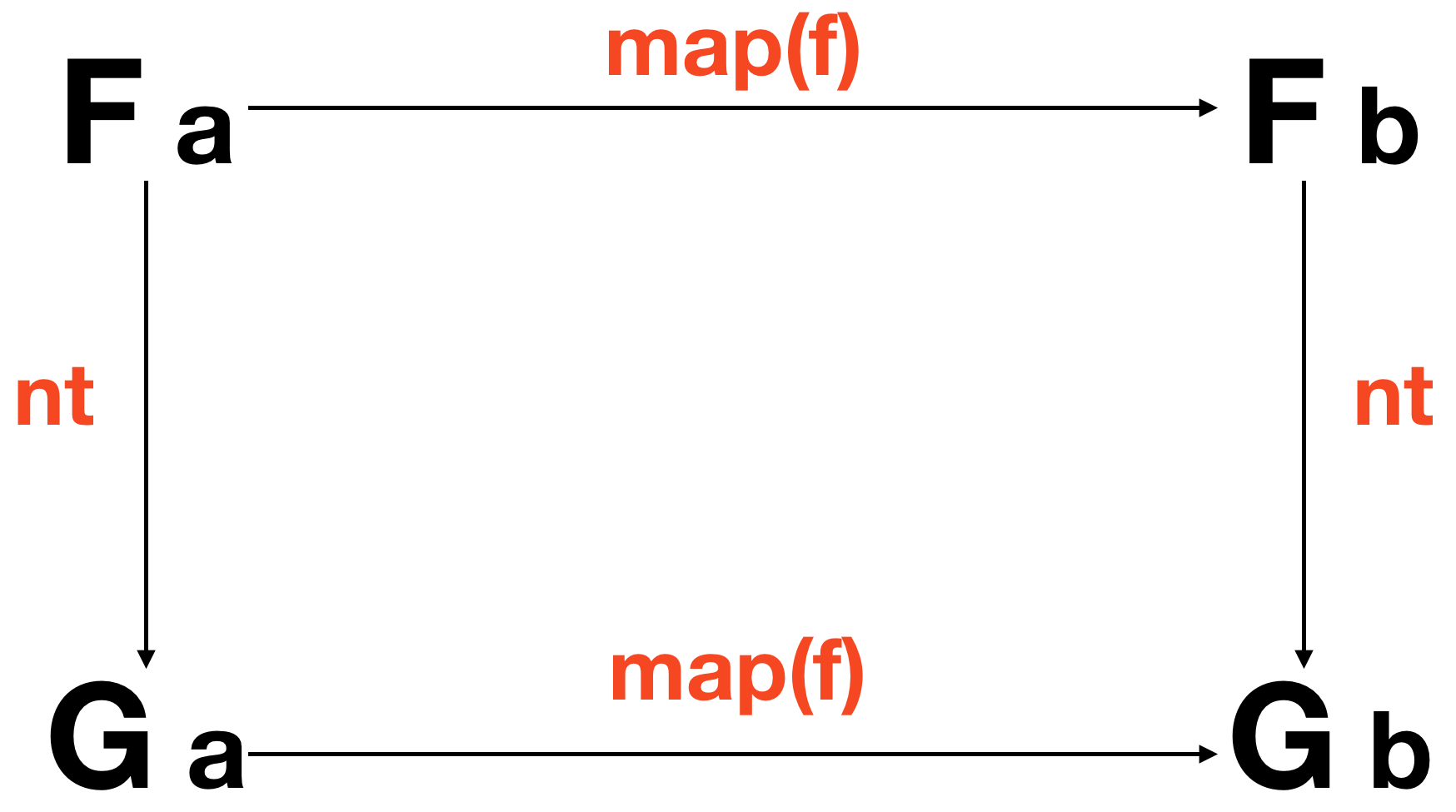
或者代码:
// nt :: (Functor f, Functor g) => f a -> g a
compose(map(f), nt) === compose(nt, map(f));
两者都体现了同样的东西:我们可以先自然变换再map,或者先map再自然变换,结果都是一样的。顺便,在 free theorem 中,也提到,自然变换不仅局限于函数和类型(以及 functor)。
# 有原则的类型转换
作为程序员,我们对类型转换十分熟悉。我们经常把String转换成Boolean,或者Integer 转换成Float(虽然JavaScript只有Number)。这些类型之间的区别很简单,这些类型都是一些代数容器,我们手头有一些可以运用的理论。
以下是一些例子:
// idToMaybe :: Identity a -> Maybe a
const idToMaybe = x => Maybe.of(x.$value);
// idToIO :: Identity a -> IO a
const idToIO = x => IO.of(x.$value);
// eitherToTask :: Either a b -> Task a b
const eitherToTask = either(Task.rejected, Task.of);
// ioToTask :: IO a -> Task () a
const ioToTask = x => new Task((reject, resolve) => resolve(x.unsafePerform()));
// maybeToTask :: Maybe a -> Task () a
const maybeToTask = x => (x.isNothing ? Task.rejected() : Task.of(x.$value));
// arrayToMaybe :: [a] -> Maybe a
const arrayToMaybe = x => Maybe.of(x[0]);
看到了吗?这些只是从一个 functor 换到了另一个。在转换过程中的数据丢失是被允许的,只要要被map的数据在转换(shape shift shuffle)中不会消失即可。这就是重点,map必须以定义执行,就算在转换之后。
从另一个角度来看,转换的是某个作用(effects)。由此可以认为,ioToTask就是从同步到异步的转换,和arrayToMaybe是从非确定性到可能失败。要注意的是,在JavaScript 里,并不能把异步变到同步,无法实现taskToIO方法,那是个"超自然"变换。
# 方法狂
假设要使用一些其他类型的方法(feature),比如对一个List进行sortBy。Natural Transformations 提供了变换为目标类型的巧妙方式,只要该类型支持map操作。
// arrayToList :: [a] -> List a
const arrayToList = List.of;
const doListyThings = compose(sortBy(h), filter(g), arrayToList, map(f));
const doListyThings_ = compose(sortBy(h), filter(g), map(f), arrayToList); // law applied
捏一把鼻子,颠三下魔杖,放进arrayToList,当当当当,[a]变成了List a,甚至还可以对其sortBy。
此外,如doListyThings_所示,将映射操作map(f)移到 Natural Transformations 的左边,更加容易实现函数的优化或者复合。
# 同构的 JavaScript
当把一个值前后怎么转换都不会丢失任何数据时,可称之为 同构(isomorphic) 。看上去挺高大上,不过就是“保持相同的数据”而已。如果两个类型在 Natural Transformations 中既可以to也可以from ,就被称之为是 同构 ,证明如下:
// promiseToTask :: Promise a b -> Task a b
const promiseToTask = x => new Task((reject, resolve) => x.then(resolve).catch(reject));
// taskToPromise :: Task a b -> Promise a b
const taskToPromise = x => new Promise((resolve, reject) => x.fork(reject, resolve));
const x = Promise.resolve('ring');
taskToPromise(promiseToTask(x)) === x;
const y = Task.of('rabbit');
promiseToTask(taskToPromise(y)) === y;
证毕。
Promise与Task是 同构 Isomorphic 。也可以实现方法listToArray使之与arrayToList构成 同构Isomorphism。反之,与 arrayToMaybe无法 同构 Isomorphism,因为转换时有数据丢失。
// maybeToArray :: Maybe a -> [a]
const maybeToArray = x => (x.isNothing ? [] : [x.$value]);
// arrayToMaybe :: [a] -> Maybe a
const arrayToMaybe = x => Maybe.of(x[0]);
const x = ['elvis costello', 'the attractions'];
// 不 isomorphic
maybeToArray(arrayToMaybe(x)); // ['elvis costello']
// 但是是一个 natural transformation
compose(arrayToMaybe, map(replace('elvis', 'lou')))(x); // Just('lou costello')
// ==
compose(map(replace('elvis', 'lou'), arrayToMaybe))(x); // Just('lou costello')
这就是 Natural Transformations,然而,因为两边的map都得到相同的结果。行文到本章的一半,似乎已经将 Isomorphic 说的差不多了,但是可别被这些表象所迷惑,真正的 Isomorphic 比我们想象的要广泛,有用的多。话不多说,让我们继续。
# 更加宽泛的定义
这些结构函数绝不仅仅局限于类型转换。 以下是一些不同的例子:
reverse :: [a] -> [a]
join :: (Monad m) => m (m a) -> m a
head :: [a] -> a
of :: a -> f a
Natural Transformations 的法则同样适用于上述方法。其中可能让你有点疑惑的是,head :: [a] -> a可以被看做成head :: [a] -> Identity a。在其中的任何地方,都可以插入Identity,因为a与Identity a为 Isomorphic。(看,我说过 Isomorphic 用途很广泛吧)
# 实现单层嵌套的方法
回到之前的场景。在其中试试 Natural Transformations,使调用中的各个类型统一化,从而可以将函数join起来。
// getValue :: Selector -> Task Error (Maybe String)
// postComment :: String -> Task Error Comment
// validate :: String -> Either ValidationError String
// saveComment :: () -> Task Error Comment
const saveComment = compose(
chain(postComment),
chain(eitherToTask),
map(validate),
chain(maybeToTask),
getValue('#comment'),
);
这里具体的操作仅仅加入了chain(maybeToTask)和chain(eigherToTack)。都是同样的效果。在join时很自然的将Task的 functor 转换到另一个Task的 functor。就像窗边的尖刺驱鸟器,从源头扼杀了嵌套。就像他们巴黎(city of the light)人说的:“Mieux vaut prévenir que guérir” - 花一英镑去治疗不如花一盎司用于预防。
# 总结
Natural Transformations 是操作 functor 的方法。在范畴学中是非常重要的概念,特别是采用多种抽象化机制时,就会用的更多。上述例子,仅仅局限于几个具体的应用中。如上文所言,只要转换类型时,确保可组合性,即可以实现所需要的不同作用 effects。同时可以解决嵌套问题,虽然会将类型同化到最低的共同母类(lowest common denominator),在实际应用中,一般是作用最易变的函子(通常是Task )(functor with most volatile effects)。
这种连续而冗长的类型是实现的代价 - 从以太中召唤而来。当然,隐式作用(implicit effects)更有潜在风险,所以也算是合理的方案。不过,如果想归并大量类型,还需要更多的工具。之后,我们将通过 Traverable 讨论重组类型。
Chapter 12: Traversing the Stone
# 练习
{% exercise %}
写一个 natural transformation 将Either b a转换到Maybe a
{% initial src="./exercises/ch11/exercise_a.js#L3;" %}
// eitherToMaybe :: Either b a -> Maybe a
const eitherToMaybe = undefined
{% solution src="./exercises/ch11/solution_a.js" %} {% validation src="./exercises/ch11/validation_a.js" %} {% context src="./exercises/support.js" %} {% endexercise %}
// eitherToTask :: Either a b -> Task a b
const eitherToTask = either(Task.rejected, Task.of)
{% exercise %}
使用eitherToTask, 简化findNameById方法, 去掉嵌套的Either。
{% initial src="./exercises/ch11/exercise_b.js#L6;" %}
// findNameById :: Number -> Task Error (Either Error User)
const findNameById = compose(
map(map(prop('name'))),
findUserById
)
{% solution src="./exercises/ch11/solution_b.js" %} {% validation src="./exercises/ch11/validation_b.js" %} {% context src="./exercises/support.js" %} {% endexercise %}
友情提示,以下方法可用于解练习题
split :: String -> String -> [String]
intercalate :: String -> [String] -> String
{% exercise %} 写出 String 和 [Char]的 Isomorphic。
{% initial src="./exercises/ch11/exercise_c.js#L8;" %}
// strToList :: String -> [Char]
const strToList = undefined
// listToStr :: [Char] -> String
const listToStr = undefined
{% solution src="./exercises/ch11/solution_c.js" %} {% validation src="./exercises/ch11/validation_c.js" %} {% context src="./exercises/support.js" %} {% endexercise %}